The electric vehicle revolution has moved beyond drivetrains and batteries to materials and manufacturing. As demand for electric transport grows manufacturers are using sustainable materials to reduce their production lifecycle impact. These are changing the performance, durability and design of next gen EVs as well as helping OEMs meet their climate targets.
The following are ten of the most eco-friendly materials for the electric vehicles of the future, as of 2025:
1. Repurposed aluminum

Recycled aluminum isn’t the only part of the next-gen EV equation, though. It’s resistant to corrosion and lightweight and cuts down on carbon emissions from manufacturing.
Traditional aluminum requires high-energy smelting, but using post-consumer aluminum slashes energy use by over 90%. Car manufacturers, including Tesla, BMW, and Audi, are ramping up their usage of recycled aluminum – for vehicle frames, as well as body panels – for their upcoming electric vehicles, indicating a strong push for sustainable materials.
2. Bio-Based Plastics

Plastics made from bio-materials, including plants, corn starch, sugarcane and algae, are replacing petroleum-based polymers. These environmentally friendly materials produce fewer greenhouse gases during the manufacturing process and biodegrade more quickly. Next gen electric vehicles are incorporating bio-plastics that are being used in interior panels, seat cushions and dashboards from companies like Ford and Toyota. This helps producers meet their sustainability goals without sacrificing style or safety.
3. Natural Fiber Composites

Natural fiber composites—derived from hemp, flax, jute, and kenaf—offer durability, sound insulation, and weight savings, making them ideal for next-generation EVs. These sustainable materials are now being used in door panels, trunk liners, and insulation layers. Both BMW’s i3 and Mercedes-Benz’s EQ line have incorporated the composites in their cars. Not only is natural fiber composite recyclable, it can also make vehicles lighter and improve energy efficiency of next-generation EVs.
4. Recycled Carbon Fiber

Recycled carbon fiber is also making inroads in EV design, thanks in part to its impressive strength-to-weight ratio, as well as to its circularity potential. Conventional carbon fiber is pricey and energy-intensive, but recycled versions offer a lower-carbon option that offers sustainability in the design and performance of e-mobility vehicles of the future. The sustainable materials are applied in the roof elements, battery enclosures and other structural reinforcements. SGL Carbon and Toray are the leading manufactures advocating this green breakthrough for the next generation of Electric Vehicles (EVs).
5. Eco-Leather Alternatives
Vegan and eco-leather substitutes are transforming EV interiors with cruelty-free, biodegradable options. Derived from pineapple leaves (Piñatex), apple peels, and mushroom mycelium, these sustainable materials offer luxury and comfort for next-generation EVs without the environmental footprint of traditional leather. Brands like Polestar, Fisker, and Lucid Motors now offer interiors made entirely of animal-free materials, setting new benchmarks in sustainable automotive design.
6. Bamboo-Based Components
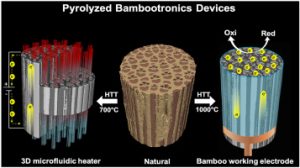
Bamboo is rapidly emerging as a renewable resource used in trim panels, flooring, and even dashboard elements. As one of the fastest-growing plants on Earth, bamboo offers excellent tensile strength and biodegradability, making it a perfect fit for next-generation EVs. These sustainable materials are lightweight, carbon-negative, and easy to process, helping reduce the overall ecological impact of vehicle production.
7. Recycled Steel

Recycled steel plays a critical role in creating the durable frames of next-generation EVs. Steel is one of the most recycled materials globally, and its reuse in automotive applications reduces the need for virgin ore extraction, conserving energy and resources. Leading manufacturers like Tata Motors and Hyundai are now integrating high-strength recycled steel in their next-generation EVs, reinforcing the importance of circular economy practices and sustainable materials.
8. Cork and Recycled Rubber

Cork and recycled rubber are innovative sustainable materials being tested for soundproofing, insulation, and seating solutions in next-generation EVs. Cork is biodegradable, lightweight, and harvested without damaging trees, while recycled rubber from tires helps reduce landfill waste. EV companies are incorporating these elements into floor mats, padding, and vibration dampeners, creating safer and quieter next-generation EVs with lower environmental impact.
9. Cellulose-Based Foams

Cellulose-based foams derived from plant fibers are emerging as eco-friendly substitutes for polyurethane and polystyrene in EVs. These foams are used for seat padding, thermal insulation, and shock absorption. As sustainable materials, they contribute to lowering emissions and reducing microplastic pollution. The adoption of cellulose foams in next-generation EVs supports cleaner production cycles and aligns with green manufacturing goals across the EV industry.
10. Ocean Plastic and Waste-Derived Polymers

Upcycling ocean plastic and industrial waste into automotive-grade polymers is revolutionizing how next-generation EVs are designed. BMW’s iX and MINI models now use parts made from recycled marine waste, while Nissan and Volvo are investing in polymers derived from end-of-life tires and packaging materials. These sustainable materials close the loop in the supply chain, giving waste a second life while lowering the carbon footprint of next-generation EVs.
The Strategic Role of Sustainable Materials in EV Manufacturing
The global push toward sustainability is reshaping automotive supply chains. Using sustainable materials in next-generation EVs goes beyond environmental stewardship—it also drives performance, durability, and consumer appeal. With governments mandating green procurement and ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) benchmarks becoming industry norms, EV manufacturers are being incentivized to innovate with purpose.
Automakers are partnering with green tech startups, materials scientists, and recycling firms to source and validate sustainable materials. These efforts are not only enhancing the lifecycle value of next-generation EVs but also ensuring compliance with international standards such as ISO 14001 and the European Union’s End-of-Life Vehicles Directive.
Key Benefits of Using Sustainable Materials in Next-Generation EVs
The shift toward sustainable materials in next-generation EVs is driven by numerous advantages:
- Lower Carbon Footprint: Manufacturing emissions are reduced through recycled and low-energy input materials.
- Weight Reduction: Lighter materials mean longer range and better battery efficiency.
- Recyclability: Components can be reused or upcycled, supporting the circular economy.
- Improved Health Standards: Use of non-toxic, bio-based inputs improves indoor air quality.
- Consumer Demand: Eco-conscious buyers increasingly prefer brands using sustainable materials in their next-generation EVs.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Sustainable EV Design
By 2030, it is estimated that nearly 70% of an EV’s material composition could come from sustainable materials. This transition is already underway, with startups and global giants alike committing to carbon neutrality. For instance, Volvo plans to use 25% recycled plastics in every car by 2025, and GM has pledged to remove all tailpipe emissions from new light-duty vehicles by 2035—an effort that depends heavily on the adoption of sustainable materials in next-generation EVs.
In India, initiatives like the “Green Mobility Mission” and FAME III are expected to promote localized development and usage of eco-friendly materials. This is likely to spur innovation among Indian EV component suppliers who are working on sustainable materials tailored for regional needs in next-generation EVs.
Conclusion
As the global EV landscape accelerates toward a sustainable future, the integration of sustainable materials in next-generation EVs is no longer optional—it’s inevitable. From recycled aluminum to ocean plastic and from bamboo to natural fiber composites, the choices automakers make today will shape the durability, efficiency, and ecological impact of the EVs of tomorrow.
By choosing sustainable materials, manufacturers can reduce lifecycle emissions, support circular economies, and align with consumer values. For next-generation EVs, this isn’t just good practice—it’s a competitive advantage. The road to a greener tomorrow is being paved with the very materials that define it.

