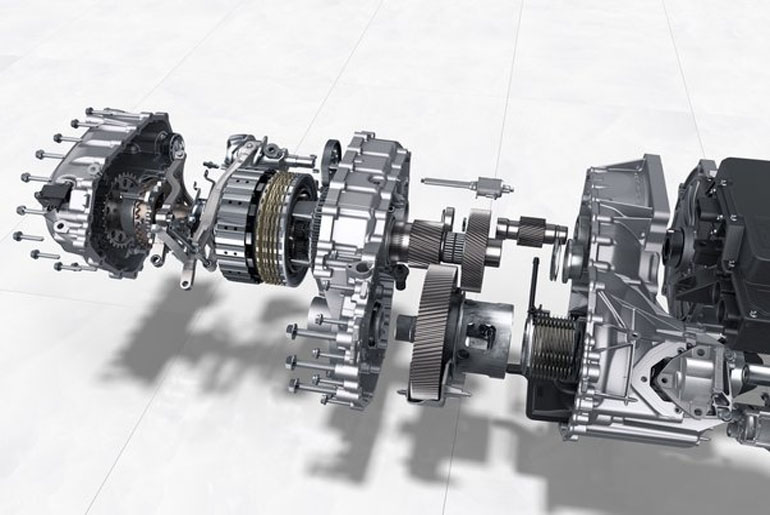
Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant attention not only for their environmental benefits but also for their impressive acceleration capabilities. Unlike traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, which rely on multi-speed transmissions to deliver power to the wheels, most EVs use a single-speed transmission. However, the role of transmission technology in EV acceleration is complex and evolving, influencing everything from efficiency to performance. This article explores how different transmission technologies impact EV acceleration, examining both current practices and emerging innovations.
The Basics of EV Powertrains
To understand how transmission technology influences EV acceleration, it’s essential first to grasp the basics of an EV powertrain. In a typical EV, the electric motor generates torque, which is then delivered to the wheels through a transmission system. Unlike ICE vehicles, where the engine’s power output varies significantly across different speeds, an electric motor delivers peak torque almost instantaneously, starting from zero RPM. This characteristic enables rapid acceleration, a key selling point for many EVs.
Single-Speed Transmissions: Simplicity and Efficiency
Most modern EVs, including popular models like the Tesla Model 3 and Nissan Leaf, use a single-speed transmission. The simplicity of a single-speed gearbox offers several advantages:
- Instantaneous Torque Delivery: With a single-speed transmission, the electric motor’s torque is directly applied to the wheels without the delay of shifting gears. This results in a smoother and more immediate acceleration, a distinct characteristic of EVs that many drivers appreciate.
- Reduced Complexity: A single-speed transmission reduces the mechanical complexity of the powertrain. Fewer moving parts mean less potential for mechanical failure, lower maintenance costs, and improved overall vehicle reliability.
- Efficiency: Single-speed transmissions are generally more efficient because they minimize energy losses associated with gear shifting and reduce friction. This efficiency translates into better range and performance.
However, the simplicity of single-speed transmissions comes with trade-offs, particularly at higher speeds where the motor must work harder to maintain acceleration, potentially reducing efficiency.
Multi-Speed Transmissions: Addressing High-Speed Performance
While single-speed transmissions are effective for most driving conditions, they are not always the best solution for every scenario. At high speeds, an electric motor’s efficiency can drop, leading to reduced acceleration and increased energy consumption. Multi-speed transmissions offer a potential solution to this challenge:
- Enhanced High-Speed Acceleration: A multi-speed transmission allows the motor to operate within its optimal efficiency range across a wider spectrum of speeds. By shifting gears, the motor can maintain better acceleration and efficiency at higher speeds, where a single-speed transmission might struggle.
- Energy Efficiency: By enabling the motor to operate in its optimal RPM range more consistently, multi-speed transmissions can improve overall energy efficiency. This is particularly beneficial for highway driving, where sustained high speeds can otherwise lead to significant energy losses.
- Improved Performance for Heavy Vehicles: For heavy-duty EVs, such as trucks and buses, the additional torque provided by lower gears can be crucial for acceleration under load. Multi-speed transmissions can offer the necessary flexibility to handle varying load conditions without compromising efficiency.
Examples of EVs utilizing multi-speed transmissions include the Porsche Taycan, which features a two-speed gearbox on the rear axle. The first gear provides quick acceleration, while the second gear is used for efficient cruising at higher speeds.
Emerging Innovations: Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) and Advanced Gear Systems
Beyond traditional multi-speed gearboxes, other transmission technologies are being explored to enhance EV acceleration:
- Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs): CVTs offer a seamless range of gear ratios, allowing the electric motor to operate at its most efficient point regardless of the vehicle’s speed. This technology can provide both smooth acceleration and high efficiency, although its application in EVs is still in the experimental stages.
- Dual-Clutch Transmissions (DCTs): DCTs offer lightning-fast gear shifts with minimal interruption in power delivery. While more common in performance-oriented ICE vehicles, there is potential for adapting DCTs to high-performance EVs to optimize acceleration across a broader range of speeds.
- Advanced Software Control: Modern EVs rely heavily on software to manage power delivery and optimize performance. Advanced algorithms can simulate the benefits of a multi-speed transmission by dynamically adjusting the motor’s power output, effectively mimicking the effects of gear shifts without the need for additional mechanical components.
The Future of EV Transmission Technology
As EV technology continues to evolve, the role of transmissions in influencing acceleration will likely expand. Innovations in battery technology, power electronics, and motor design will play a significant role in determining the optimal transmission strategy for future EVs.
For instance, as batteries become more energy-dense and motors more efficient, the need for multi-speed transmissions may diminish for certain applications. On the other hand, as EVs are increasingly used in diverse scenarios—from high-performance sports cars to heavy-duty trucks—tailored transmission solutions may become more prevalent.
Moreover, the integration of smart technologies, such as predictive algorithms and adaptive control systems, could further optimize the balance between acceleration and efficiency, pushing the boundaries of what EVs can achieve.
Conclusion
Transmission technology plays a pivotal role in shaping the acceleration characteristics of electric vehicles. While the simplicity of single-speed transmissions has driven the initial wave of EV adoption, the demands for higher performance, efficiency, and versatility are leading to a renewed interest in multi-speed and advanced transmission systems. As the EV market matures, ongoing innovations in transmission technology will continue to influence how these vehicles accelerate, ultimately contributing to the broader adoption of electric mobility and the realization of its full potential.