Electric vehicles (EVs) are growing quickly around the world. India is making progress with government policies and state incentives. However, long charging times continue to be a major issue. Standard home AC chargers work well for overnight charging, but they do not meet the needs of long trips or large battery packs. This makes them unsuitable for commercial fleets. DC fast charging addresses this issue by delivering strong direct current (DC) to the battery. This method greatly cuts down charging time and enables faster, easier EV charging for both private owners and fleet operators.
What is DC Fast Charging?
DC fast charging is a method to charge electric vehicles using direct current (DC) instead of alternating current (AC). Most home and workplace chargers use AC electricity from the grid. These chargers depend on the car’s onboard charger to convert AC to DC before it reaches the battery. In contrast, DC fast charging converts AC to DC outside, at the charging station, and sends it directly to the vehicle’s battery. This process bypasses the limitations of onboard chargers, allowing for much higher charging currents and significantly reducing charging times.
The charging speed of DC fast charging surpasses traditional AC charging because it requires only 20–40 minutes to bring an EV battery from zero to 80% while the charging speed depends on the power output and battery size. The fastest chargers which deliver 250–350 kW power levels can achieve 80% battery capacity in less than 20 minutes provided the vehicle supports such charging rates.
Key Features:
1. High Power Output
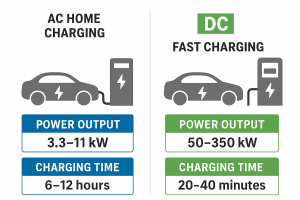
The main feature is its high power delivery capacity. Standard DC fast chargers provide power from 50 kW to 350 kW. In contrast, typical residential AC chargers deliver power between 3.3 and 11 kW. This difference shows that DC fast charging can charge an EV much faster than standard AC chargers.
2. Rapid Charging
The main goal of this charger is to quickly charge 40 to 60-kWh mid-range EV batteries to 80% in 20 to 40 minutes.The electric vehicle charging technology known as DC fast charging minimizes downtime for vehicles with bigger batteries such as SUVs and commercial trucks thus making electric vehicles more practical for extended trips and business operations.
3. External Conversion
The onboard AC-to-DC conversion process in AC chargers limits the charging speed while DC fast charging performs this conversion within the charging station itself. The elevated current output through this method significantly decreases charging times and boosts operational efficiency.
4. Connector Specifications
The compatibility of DC fast charging needs specific connector standards for proper operation. The most common are:
- CCS (Combined Charging System): This charging standard applies to EVs in Europe, America, and India.
- CHAdeMO: This charging protocol is popular among Japanese electric vehicles, including Nissan models.
- Tesla Supercharger (exclusive): This charging system enables fast charging at Tesla Supercharger stations and is only compatible with Tesla vehicles.
For EV owners to access DC fast charging stations that fit their vehicle specifications, it is essential to understand these standards.
Benefits
Time Effectiveness
The main benefit is its speed. Long charging times have been a big problem for electric vehicle owners, especially during road trips or for commercial fleets. With DC fast charging, drivers can quickly recharge their batteries. This lets them travel longer distances with less interruption.
Convenience
For fleet operators and daily commuters, DC fast charging reduces waiting times from several hours to just minutes. This convenience creates a smoother and more flexible electric mobility experience.
Supports Large Batteries
As SUVs and trucks with larger battery packs become more common, DC fast charging makes sure that even high-capacity batteries charge efficiently. This is especially helpful for businesses, where time matters.
Drawbacks
DC fast charging has certain drawbacks despite its benefits:
- High Installation Costs: Installing a DC fast charging station can cost between ₹15 lakh and ₹50 lakh or more, depending on power output and infrastructure needs.
- Battery Degradation: Frequent use of high-power DC fast charging can produce heat and a high current flow, which may shorten the battery’s lifespan.
- Grid Load: High-power chargers use a large amount of electricity, which may sometimes require upgrades to the grid.
- Not Suitable for Home Use: Due to cost, high power demands, and space requirements, it is mostly found in public stations, on highways, and at fleet depots.
DC Fast Charging in India
To support long-distance drivers and commercial vehicles, India is gradually introducing DC fast charging. The market for electric vehicles is expanding rapidly. Many companies are installing DC fast chargers along highways and in cities. Some of these companies include Tata Power EZ Charge, ABB, Delta Electronics, Ather Grid, and EVgo.
In India, most passenger EVs, including the Tata Nexon EV, MG ZS EV, and BYD Atto 3, are capable of 50 kW to 100 kW DC fast charging. Future EV models may increasingly support 150 kW or higher rates as ultra-fast chargers become more common. This will reduce charging times and enable smoother long-distance travel.
How DC Fast Charging is Transforming Indian EV Adoption
Fast charging stations that use DC power are essential for the growth of electric vehicles in India. Having quick charging stations through DC fast charging helps drivers deal with ‘range anxiety’ since they can charge their vehicles quickly on major routes and highways. The increased confidence of consumers and businesses leads them to consider EVs as a practical alternative to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
The operational duration of delivery trucks and taxis as well as ride-sharing vehicles experiences significant improvement through DC fast charging which benefits commercial fleets. India propels its sustainable urban transportation goals and national carbon emission targets through this program.
Comparing DC Fast Charging with AC Home Charging
| Feature | AC Home Charging | DC Fast Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Power Output | 3.3–11 kW | 50–350 kW |
| Charging Time (0–80%) | 6–12 hours | 20–40 minutes |
| AC-to-DC Conversion | Inside EV onboard charger | Inside charging station |
| Suitable Location | Home, workplace | Highways, commercial stations |
| Cost of Installation | Moderate (~₹25k–₹80k) | Very high (~₹15–50 lakh+) |
AC home charging works best for daily travel requirements and overnight charging yet DC fast charging enables fast battery charging for longer trips. The combination of these charging methods creates a flexible and reliable power delivery system which benefits electric vehicle drivers.
The Future of DC Fast Charging in India
The quick expansion of electric vehicles in India makes DC fast charging an essential part of the transportation system. The DC fast charging network expands through state and private sector investments and partnerships between electric vehicle manufacturers and energy companies. Future advancements may include high-power charging stations that exceed 350 kW power levels along with smart charging systems connected to renewable power sources and V2G capabilities which optimize energy utilization.
The future electric vehicle plan for India heavily relies on the development of DC fast charging stations that service both highway routes and high-density city areas. The development of technology will reduce costs and improve performance while enhancing vehicle model compatibility thus making DC fast charging an essential part of India’s sustainable mobility future.
Conclusion
The EV fast charging market in India has experienced substantial growth because of advancements in both battery technology and charging technology. The increased adoption of electric vehicles throughout India has led to more demand for fast charging stations. Electric vehicle manufacturers and service providers in India have made significant investments to establish DC fast charging infrastructure which is growing at an annual rate of 50 percent.
India is establishing a sustainable electric mobility system through public fast charging network investments and their placement in urban development and highway infrastructure projects. The growing availability of EV models with high-power charging compatibility will establish DC fast charging as the foundation of India’s EV infrastructure thus making electric vehicles practical for all users while addressing range anxiety concerns.

