The modern automobile is no longer just a mode of transportation, it’s a hub of intelligence, connectivity, and real-time data exchange. As vehicles evolve into software-defined platforms, the need for a scalable, high-speed, and robust in-vehicle communication network becomes paramount. Automotive Ethernet has emerged as the cornerstone of next-generation vehicle architecture, enabling seamless communication between various vehicle subsystems.
From infotainment systems to advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), single Pair Ethernet is quickly becoming the go-to standard in automotive networks, offering lighter 2-wire cabling and greater efficiency than traditional technologies. Automotive Ethernet is a proven off-the-shelf technology that can scale to higher transmission rates as well as provide the necessary functionality required for Automotive applications via Time-Sensitive Networking and general networking standards and protocols.
What is Automotive Ethernet?
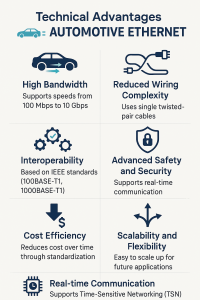
Automotive Ethernet (100BASE-T1 / 1000BASE-T1) is a set of protocols and device standards that adapt Ethernet technologies for automotive use, specifically for in-vehicle networking. It uses a single pair of unshielded twisted wires to transmit and receive data. 100BASE-T1 / 1000BASE-T1 is a physical full-duplex interface enabling transmission and reception on the same pair, unlike 10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX, where transmission and reception are on dedicated pairs.
Automotive Ethernet replaces the traditional 8-wire shielded twisted pair cabling with a smaller, 2-wire unshielded twisted pair. By simplifying to a single system and reducing the use of expensive copper and redundant network hardware, it streamlines in-vehicle communication. OABR (Open Alliance BroadR-Reach), based on the 100BASE-T1 standard, is a physical layer standard for automotive Ethernet connectivity. It enables multiple in-vehicle systems to communicate simultaneously over a single unshielded twisted-pair cable. Offering higher bandwidth, OABR is approximately 30% lighter than equivalent mainstream technologies, enhancing vehicle efficiency and cutting installation costs by up to 80%.
100BASE-T1 (100Mbps) operates at 100 Mbps and uses a combination of 4B3B, 3B2T, and PAM3 (3-level Pulse Amplitude Modulation) encoding to minimize electromagnetic interference and enable full-duplex communication. Meanwhile, 1000BASE-T1 supports 1 Gbps speeds using more advanced techniques such as PAM8 modulation, along with scrambling, echo cancellation, and equalization to ensure signal reliability over automotive-grade links. Both rely on a PHY layer that handles all encoding and decoding, making them ideal for modern in-vehicle networking applications.
In Automotive Ethernet, particularly in standards like 100BASE-T1 and 1000BASE-T1, communication is based on a Master-Slave model to ensure precise timing and synchronization. The master device generates the clock signal, which the slave device receives and achieves the time synchronization for Ethernet with the help of gPTP “generalized Precision Time Protocol”. This setup is crucial because Automotive Ethernet transmits data over a single twisted pair in full duplex, making synchronization vital for accurate communication. Typically, central units like gateways or domain controllers act as masters, while sensors, cameras, or ECUs function as slaves. This model minimizes latency and jitter, enabling reliable, real-time in-vehicle networking.

Why is Automotive Ethernet Essential in Telematics Devices?
Telematics Units and Gateways act as communication hubs in the vehicle, collecting, processing, and transmitting data between ECUs, the cloud, and external networks. As vehicle data volumes increase, traditional networks struggle to keep pace.
Automotive Ethernet is essential in telematics gateways because it provides the high bandwidth, low latency, and scalability needed to manage modern vehicle data flows. As telematics systems handle GPS, over-the-air updates, V2X communication, and integration with ADAS and infotainment, Ethernet ensures fast and reliable connectivity across all domains. It also supports advanced security features like encryption and secure boot, while enabling real-time communication through Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN). Its flexibility and future-proof nature make it the ideal backbone for evolving connected car architectures
iWave’s Telematics Solutions with Automotive Ethernet Support
iWave has built a strong portfolio of telematics solutions with extensive wired interfaces and wireless connectivity options. The Telematics Gateway from iWave is a next-generation telematics solution with extensive processing power, automotive Ethernet and 5G Connectivity.

- Telematics Gateway (iW-RainboW-G41G)
- Powered by i.MX 8XLite MPU
- 5 x CAN FD ports
- 2 x Automotive Ethernet Ports
- LTE Cat 4 and 5G Cellular Connectivity
- Wi-Fi 6 and Bluetooth Connectivity
- High Accuracy GNSS Module
- RS232, RS485, Analog and Digital IOs
- Integrated Hardware Secure Element
- Enclosure with External Antennas
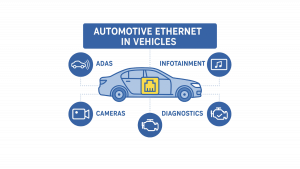
Unlike traditional automotive networking protocols such as CAN, LIN, or FlexRay, iWave’s Automotive Ethernet-enabled telematics platforms are engineered to accelerate your product development and bring future mobility solutions to life. Automotive Ethernet offers higher bandwidth, standardization, and IP-based networking, making it ideal for data-intensive applications. It allows for seamless integration of features like 360-degree cameras, over-the-air (OTA) updates, real-time diagnostics, and V2X communication, providing the backbone for both infotainment and safety systems in connected vehicles.

