As industrial and personal electronics add more advanced technologies, they create increasingly unpredictable loads on batteries, necessitating a more reliable and intelligent battery gauge. Whether in emerging artificial intelligence (AI)-enhanced devices or established systems such as drones, power tools, and robotics, batteries experience highly dynamic load profiles. These unpredictable loads create a challenge for designers who rely on accurate gauging to shut systems down safely or prevent unexpected brownouts. While an unexpected shutdown in a cordless drill may only frustrate its user, a drone falling from the sky poses a serious safety risk.
What does a battery gauge do?
Battery gauges calculate essential parameters such as state of charge, state of health, and remaining capacity using current and voltage measurements. Traditional Impedance Track™ technology-based battery gauges assume that the battery load varies slowly, which enables accurate resistance measurements while the battery is discharging to calculate a high-accuracy real-time state-of-charge prediction. Modeling the battery as a low-frequency resistor-capacitor (RC) model is sufficient for these slowly varying battery loads. However, newer applications with variable or high-frequency load currents need a more comprehensive model and adaptive algorithm to maintain accurate state-of-charge estimations.
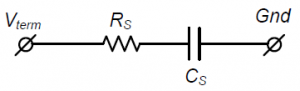
Figure 1. Low-frequency RC battery model
The Dynamic Z-Track™ algorithm is a battery-gauging method designed for devices such as the BQ41Z90 and BQ41Z50. As a successor to the traditional Impedance Track™ algorithm, which operates in devices such as the BQ40Z50 and BQ34Z100, the Dynamic Z-Track™ algorithm provides accurate state-of-charge, state-of-health, and remaining capacity estimations of batteries under dynamic load-current conditions.
When an erratic or high-frequency load impacts the battery, an Impedance Track™ gauge’s traditional RC modeling loses resolution for updating the resistance of the battery. The Dynamic Z-Track™ algorithm implements a broadband transient model that simulates voltage transients and adapts to dynamic current profiles. This approach enables real-time resistance estimations even when the current is not stable.
Why is resistance important?
Tracking resistance is essential to deliver the highest accuracy state-of-charge calculation over the entire lifetime of the battery. A battery cell’s resistance increases linearly with cycling and aging until it reaches a turning point where resistance rises exponentially toward the end of its life. Resistance also fluctuates significantly with temperature—lower temperatures result in higher resistance and, consequently, lower available capacity.
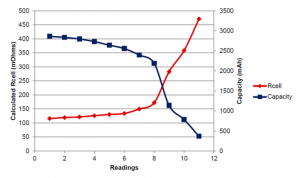
Figure 2. Resistance change of a lithium-ion battery cell over time
When the battery gauge cannot update resistance, the calculated state-of-charge error grows proportionally with battery aging. This error can range from 10% to as high as 60% without proper resistance updates under erratic loads. Users experience this as sudden drops in state of charge, leading to unexpected shutdowns due to overestimated remaining capacity as shown in figure 3.
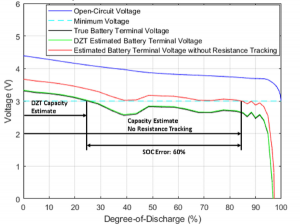
Figure 3. Remaining capacity estimation comparison: Impedance Track technology and Dynamic Z-Track
technology vs. no resistance update at a 1.75C load
Use-case example
Imagine a person riding their e-bike home. They check the state of charge, see 30% remaining, and decide to detour to the grocery store. Upon arrival, it shows 15%, but on the way home, the e-bike suddenly stops because the state of charge plummets from 12% to 0%. Now the rider must pedal home or call for help.
The Dynamic Z-Track™ algorithm prevents this situation. Unlike conventional gauges, TI’s Dynamic Z-Track™ technology delivers up to 99% state-of-charge accuracy, even under unpredictable loads. This allows manufacturers to optimize battery size and extend run time by as much as 30%, providing users with more reliable performance in demanding applications like drones, e-bikes, laptops, and portable medical devices.
Conclusion
While unpredictable battery loads pose significant design challenges, they need not limit system reliability or user experience. Tools such as the Dynamic Z-Track™ algorithm enable designs where battery-powered devices simply work — a future where drones complete flights without sudden landings and e-bikes get riders home without fail.
Authored by- TI Staff

